Enclosed Lead Screw Actuator
Overview
The enclosed lead screw is a rigid, high-force actuator for the toughest applications. Thanks to its pinch point-free configuration and fully sealed body, you can deploy it in dusty environments where other actuators can’t keep up.
The actuator is guided by four robust linear profile bearings and two guiding rails for maximum rigidity. It comes in two lengths: 855mm and 1530 mm.
Composition
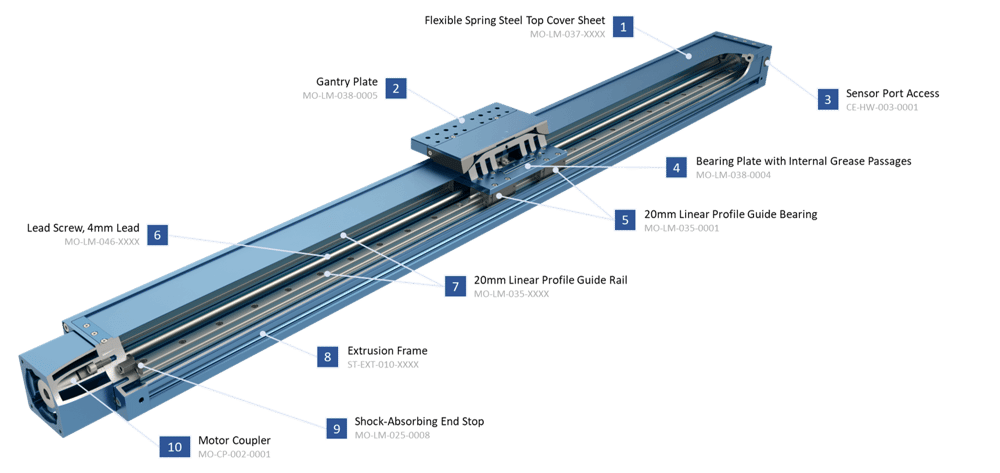
- A thin spring-steel cover seals off the top of the enclosed lead screw actuator, keeping contaminants out and eliminating pinch points. The cover is held down by magnetic strips mounted in the extrusion body.
Note: Cover is not load bearing. Do not apply a load to it, or it will break. - The 225 mm gantry plate offers 32 holes for mounting components, as well as an easy-access grease point that lubricates all moving components in the actuator at the same time.
- Sensor port access for home and end of travel detection. The ports come with pre-installed plugs.
- The bearing plate connects four linear profile guide bearings together and attaches them to the gantry plate. It also features grease passages that evenly distribute lubricant to all components.
- 20 mm linear profile guide bearings provide excellent strength and rigidity.
- The 4 mm lead screw provides rigid, and high-force actuation for extreme applications requiring self-locking.
- 20 mm linear profile guide rails locate the linear ball bearings. Two rails are installed in each actuator for maximum rigidity in all directions.
- A specially designed extrusion profile provides the outer structure, as well as mounting points for other components. The frame is 135 mm wide and 90 mm tall.
- Shock absorbing end-stops are pre-installed on the actuator; there is no need for external bump stops.
- The motor is connected to a zero-backlash coupling for efficient and accurate power transmission.
Application
The enclosed lead screw is an extremely rigid actuator and is our go to solution for lifting applications that require self-locking. The actuator can be used in horizontal and vertical configurations but is mainly used in vertical orientations.
One great use for the enclosed lead screw actuator is as a heavy payload vertical range extender. The enclosed lead screw can fully support large cobots, like the Doosan H2515 and H2017, on its own. The self-locking characteristic ensures that in the even of power loss, or brake failure, the actuator will not fall. This is why it is most used in cobot palletizing applications where maintaining safety standards are a must.
Explore public designs to get ideas on how you could use the enclosed lead screw actuator.
Technical Specifications
| Displacement ratio | 4 mm/turn |
| Force per unit of input torque (N / Nm)* | 458 |
| Maximum input torque (Nm) | 61 |
| Accuracy | 0.09 mm per 300 mm of length |
| Backdrive resistance | Self-Locking |
| Max lifting capacity | 550 kg |
| Motor compatibility | NEMA 34, 14-mm shaft with 5-mm key |
| Sensor compatibility | Vention’s Flush Inductive Proximity Sensor (CE-SN-004-0003) only |
*Note: Linear force per unit of input torque is highly dependent on internal frictional forces. Value is given as a estimate only.
Available Sizes
The enclosed lead screw actuator comes in two lengths (length refers to extrusion body length).
To calculate actuator travel, subtract 215 mm from the body length.
For example, the 855 mm actuator has a total travel of 855 mm - 215 mm = 640 mm.
| Part Number | Body Length (mm) | Total Travel (mm) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MO-LM-047-0855 | 855 | 640 | 18.30 |
| MO-LM-047-1530 | 1530 | 1315 | 27.07 |
Load Capacity
The table and figure below describe the nominal and maximum loads and moments in each direction.
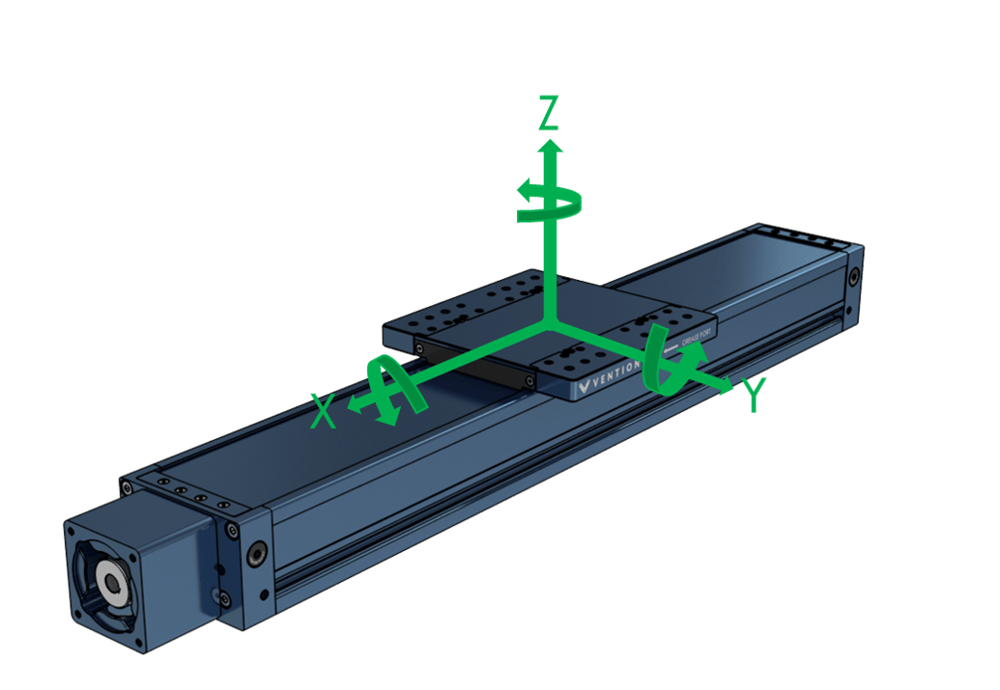
| Nominal axial force (Fx) | See driving forces |
| Max peak axial force (Fx) | See driving forces |
| Nominal roll moment (Mx) | 935 Nm |
| Max peak roll moment (Mx)* | 2000 Nm |
| Nominal horizontal force (Fy)** | 5000 N |
| Max peak horizontal force (Fy)** | 10 000 N |
| Nominal pitch moment (My) | 1630 Nm |
| Max peak pitch moment (My)* | 2500 Nm |
| Nominal vertical force (Fz)** | 5000 N |
| Max peak vertical force (Fz)** | 10 000 N |
| Nominal yaw moment (Mz) | 1630 Nm |
| Max peak yaw moment (Mz)* | 2500 Nm |
*Note that max peak values represent the absolute maximum load. Peak loads are acceptable during one-time events such as emergency stops, but operating at peak loads continuously will cause excessive wear and shorten the actuator’s lifespan.
**Note that force limitations depend on the supporting structure and the unsupported length of the actuator. Listed values are for unsupported lengths of 855 mm or less.
Driving Force
The driving force indicates how much weight the actuator can move and how quickly it can accelerate. This force is shown as “Fx” in the Load Capacity figure.
For a more in-depth explanation of driving force, see the “calculating actuator forces” section of our linear actuator selection guide, or ask a Vention Application Engineer for help.
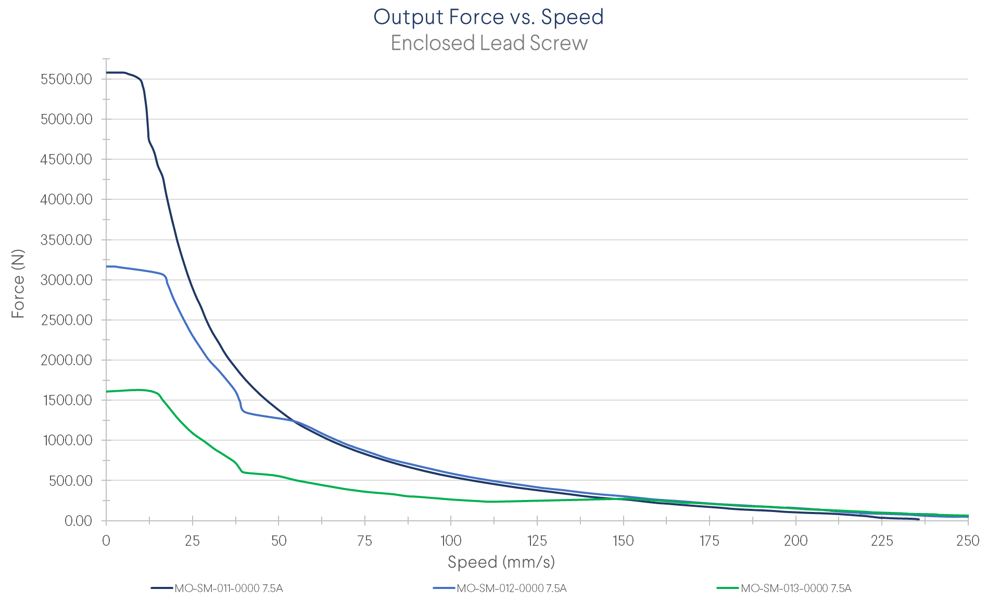
Note: During MachineMotion’s boot up sequence, the holding force is momentarily 65% of its rated value. Please keep in mind when using in vertical and/or angled applications.
Buckling and Critical Speed
In terms of load and speed, lead screws are limited in two ways beyond normal material and bearing strength.
First, when dealing with lead screws, you must consider buckling. Buckling is when a long structure (in this case, the screw) suddenly bows and deforms due to compressive load. This deformation makes the screw even less rigid and will usually lead to screw failure. Since buckling is a critical failure mode of lead screws, it is important to consider it and the loads applied to ensure it will not occur. Because buckling is such an important consideration, we use a safety factor of at least 1.5.
| Part Number | Max Permissible Compressive Load (N) |
|---|---|
| MO-LM-047-0855 | 6595.9 |
| MO-LM-047-1530 | 1810.7 |
As seen, buckling condition is never going to be an issue for the 855mm length because it exceeds the possible motor output, however the bucking load for the 1530mm actuator should be kept in mind since the motor is capable of lifting more than the screw can support.
Second, you must consider the shaft’s critical speed. This is the rotational speed at which the screw will begin to violently vibrate. This behavior is due to the screw’s harmonics, and it can damage the lead screw. The following table shows the maximum permittable operating speeds for each actuator length.
| Part Number | Max Permittable Speed (mm/s) |
|---|---|
| MO-LM-047-0855 | 235*** |
| MO-LM-047-1530 | 50 |
***Note: The max travel speed of a lead screw is limited to 50mm/s by default to avoid overspeed issues. If you have a screw shorter than the 1530mm and want to increase speed, you may configure your actuator as a “custom” type to bypass this safety limit.
For MO-LM-047-0855, the critical speed is not a concern as the critical speed is close to the maximum speed of the motor, however the 1530mm actuator will need to be limited to operation below 50 mm/s to ensure the lead screw does not reach the maximum permittable speed.
Duty Cycle
The typical duty cycle of the Enclosed Lead Screw Actuator is 25% when being used with a 50kg payload and travel speeds of 40-50mm/s. This duty cycle rating is relative to actuator load and speed. Decreasing either load or speed can increase the duty cycle and vice versa.
Exceeding this 25% duty cycle can cause heat build up and lead to increased wear and reduction in life of components and grease, reduce your lubrication interval.
For assistance in knowing if your application will respect the duty cycle or questions about the life of the lift column, please contact our application engineering specialists.
Assembly Instructions
The enclosed ball screw actuator comes completely assembled. All you need to do is install your choice of powertrain components, such as a motor and brake, and add sensors.
Notes:
- When installing motors, apply a small amount of grease to the motor shaft so that it is lightly coated. This will reduce the possibility of fretting corrosion occurring during operation, making future removal easier.
- Moreover, do not use excessive force (hammering, prying or using screws to “push” the motor) to install the motor.
i) To attach the powertrain components, push the shaft into the motor coupling. The coupling is pre-installed on the actuator.
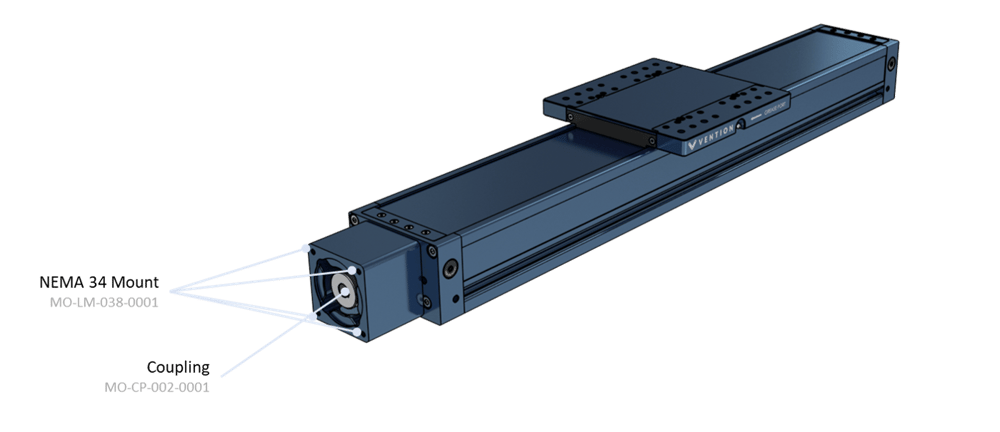
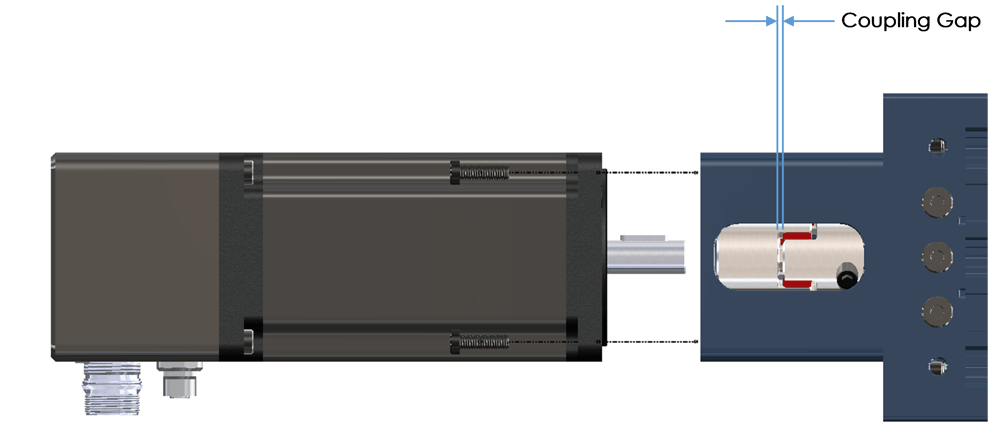
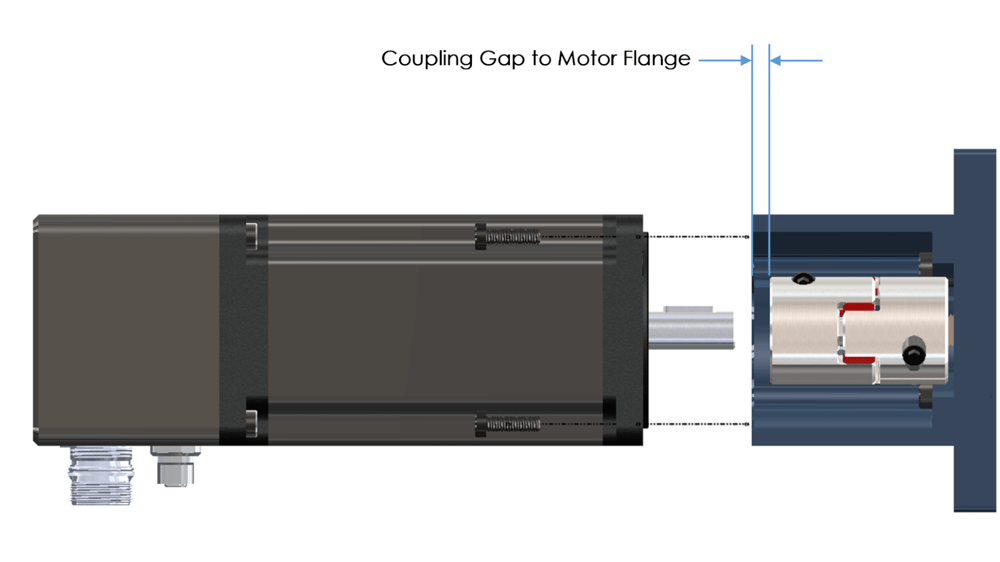
ii) Check the gaps between the coupling and the motor as shown in the following images. The coupling gap should be 1-2mm. With the motor installed check that the “coupling gap to motor flange” is not touching the motor face. Failure to properly set either gap will cause damage to the motor and or coupling.
 |
 |
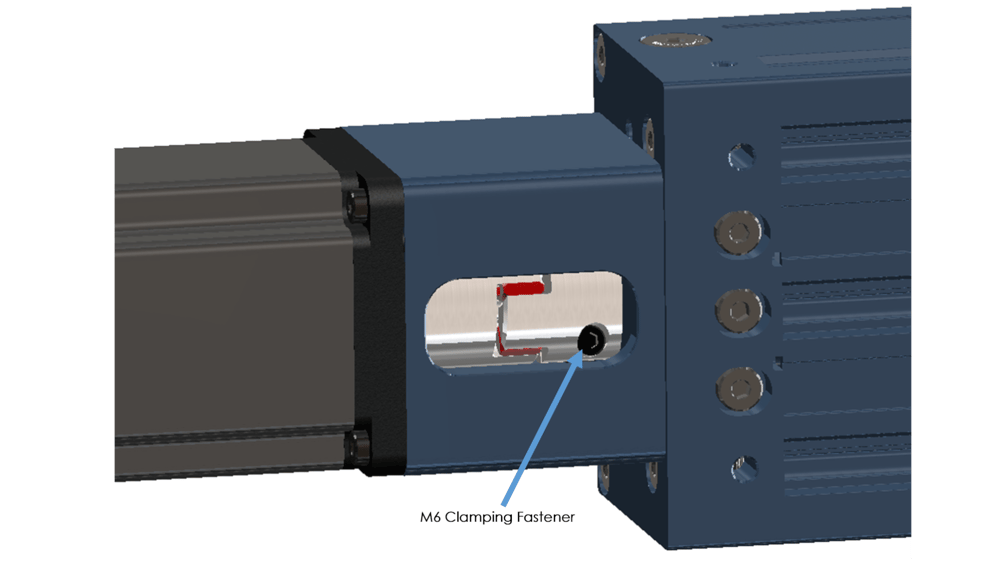
iii) After verifying the above, tighten the 4 M6 bolts that hold the motor onto the actuator, followed by the two clamping fasteners in each coupling half. During final installation, medium strength thread locker is highly recommended for the motor side clamping bolt. All M6 bolts should be torqued to 10-12Nm:
 |
 |
iv) You can install sensors in any of the four sensor port locations. To install a sensor, remove the port plug and screw the sensor all the way into the hole until it bottoms out. Unscrew the sensor by a half turn to ensure it is not compressing the bump stop. Install one jam nut and tighten it to lock the sensor in place.
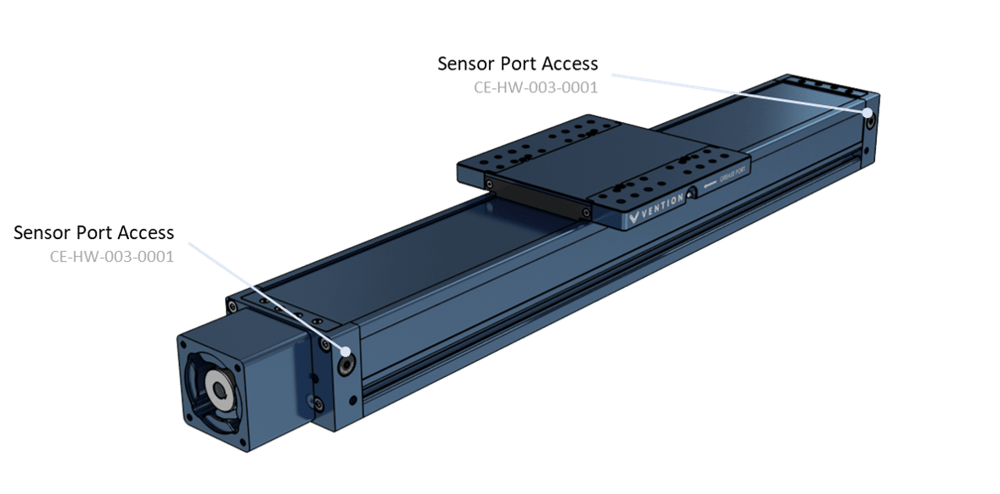
Note: Sensor ports are available on both sides of the actuator. The only sensor compatible with the actuator is the flush mount proximity sensor (CE-SN-004-0003).
v) Once the powertrain and sensors are in place, attach the actuator to your structure. Connect the actuator’s extrusion body or end plates to any appropriate structural component. To ensure sufficient rigidity, maintain a minimum support distance of 855 mm.
vi) Optional: Route cables through a drag chain. Drag chain can be installed on the gantry plate’s underside, as shown below. If you use the included M8 x 8-mm fasteners to attach the drag chain to the gantry, you can thread into the same hole from the bottom even if something is attached from the top of the gantry, expanding your drag chain installation options.
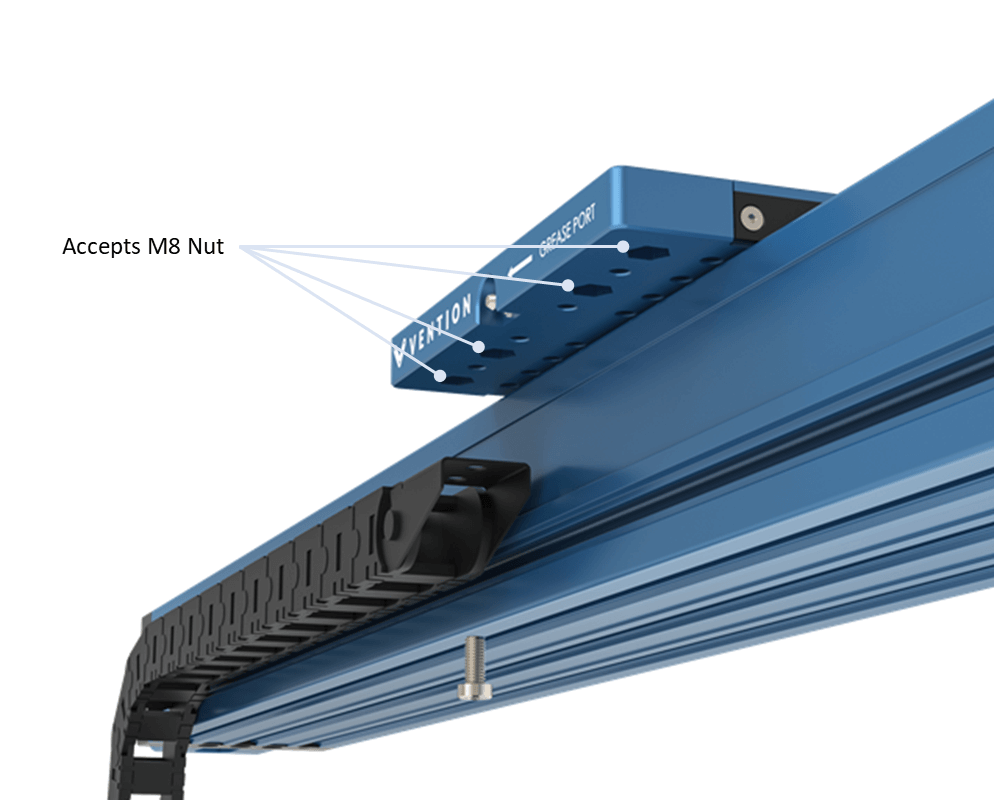
vii) Mount parts to the gantry using the threaded holes, counterbored holes or by installing nuts in the counterbored holes. The included M8 nuts easily transform the counterbored holes into threaded holes for maximum flexibility.
Note: When mounting multiple enclosed actuators in parallel, refer to the Self-Aligning Mount Technical Document.
Be sure to respect the speed limitations set out in the “Maximum Permittable Speed” section of the Technical Specifications in this document while operating or configuring this actuator.
Note: the 1530mm variant of the actuator (MO-LM-047-1530) is not currently compatible with the Vention Configuration Checker and the configuration must be done manually.
Maintenance
For maintenance instructions, please see the appropriate section in our Maintenance Technical Document.